Switchable Surfactants for Catalyst Preparation

We are interested in designing new methods of synthesizing nanocatalysts using green and sustainable techniques. Two methods we are currently investigating include the use of Switchable Surfactants to deposit bare nanoparticles onto a support or through the use of inert polymers.
One novel particle synthesis technique we use involves utilizing Switchable Surfactants (SwIS). These are molecular liquids that take on an ionic form when exposed to carbon dioxide, and then revert to their original form when heated, freeing the carbon dioxide in the process. Our current hypothesis, which is based on the original research this technique was adapted from, is that the SwIS forms micelles that act as microreactors and stabilize the nanoparticles within them. We can then revert the SwIS to its non-ionic form and release the particles, which provides surface clean particles that can be directly used for catalysis without the need for surface cleaning.
Publications:
Bryant, K., Wheeler West, C., Saunders, S.R. “Impacts of Calcination on Surface-Clean Supported Nanoparticle Catalysts” Applied Catalysis A: General, 2019, In Press.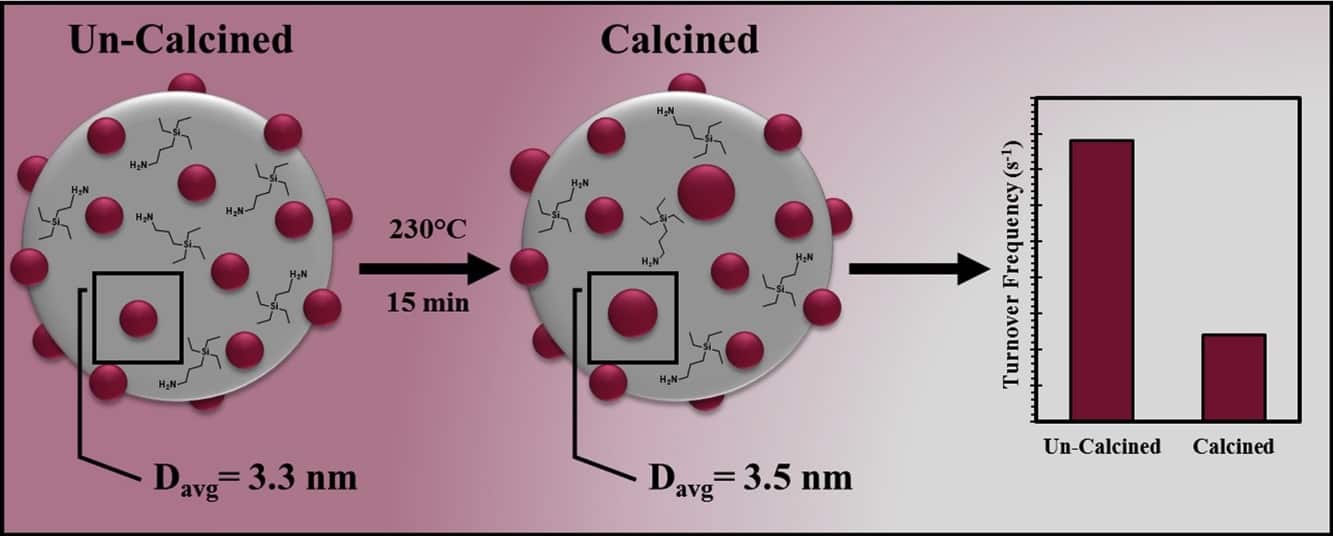 Bryant, K., Ibrahim, G., Saunders, S.R. “Switchable Surfactants for the Preparation of Monodisperse, Supported Nanoparticle Catalysts” Langmuir, 2017, 33 (45) 12982-12988.
Bryant, K., Ibrahim, G., Saunders, S.R. “Switchable Surfactants for the Preparation of Monodisperse, Supported Nanoparticle Catalysts” Langmuir, 2017, 33 (45) 12982-12988.
Funding

Collaborators
Christy Wheeler West – University of South Alabama